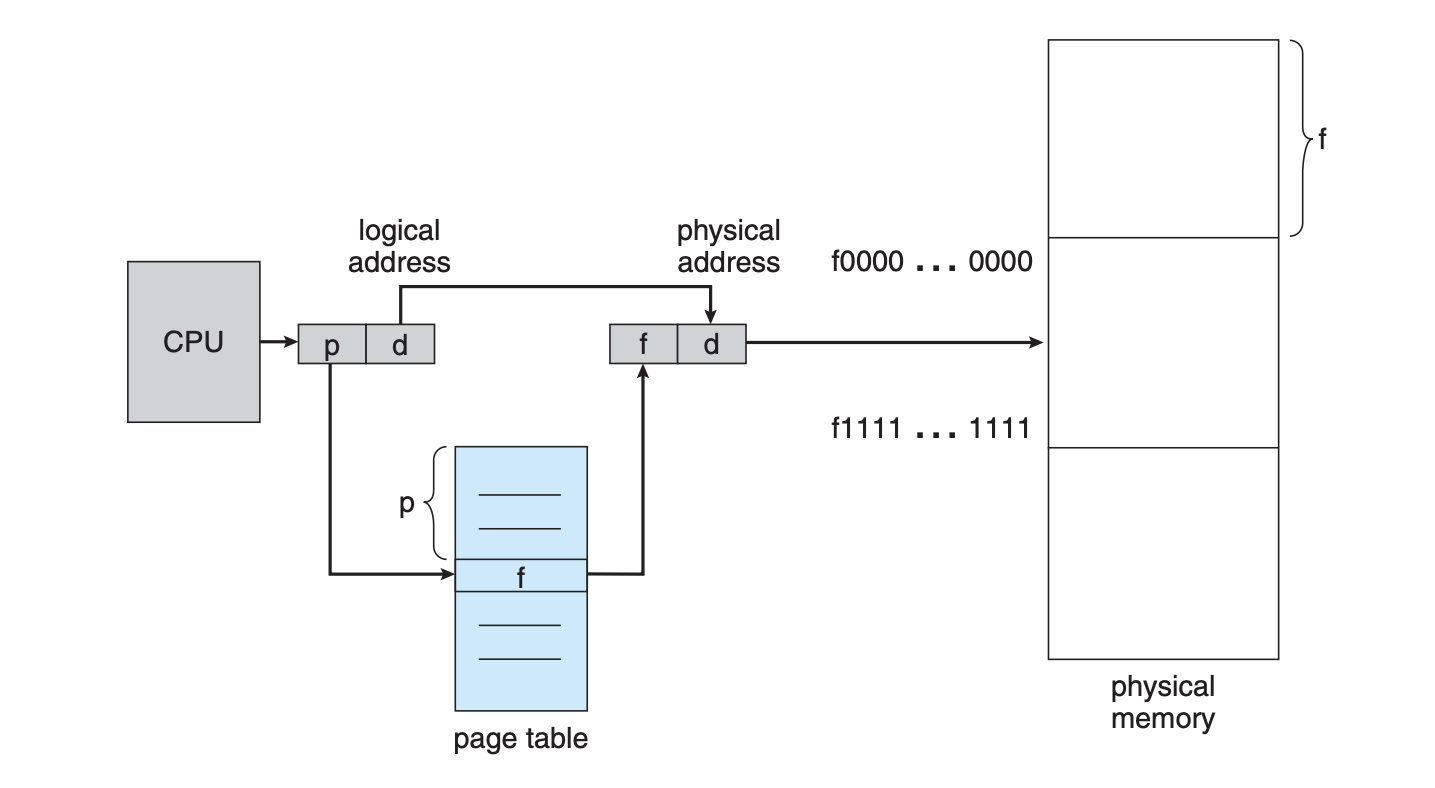
The basic method for implementing paging involves breaking physical memory into fixed-sized blocks called frames and breaking logical memory into blocks of the same size called pages. When a process is to be executed, its pages are loaded into any available memory frames from their source (a file system or the backing store). The backing store is divided into fixed-sized blocks that are the same size as the memory frames or clusters of multiple frames. This rather simple idea has great functionality and wide ramifications. For example, the logical address space is now totally separate from the physical address space, so a process can have a logical 64-bit address space even though the system has less than 264 bytes of physical memory.Every address generated by the CPU is divided into two parts: a page number (p) and a page offset (d). The page number is used as an index into a page table. The page table contains the base address of each page in physical memory. This base address is combined with the page offset to define the physical memory address that is sent to the memory unit.
